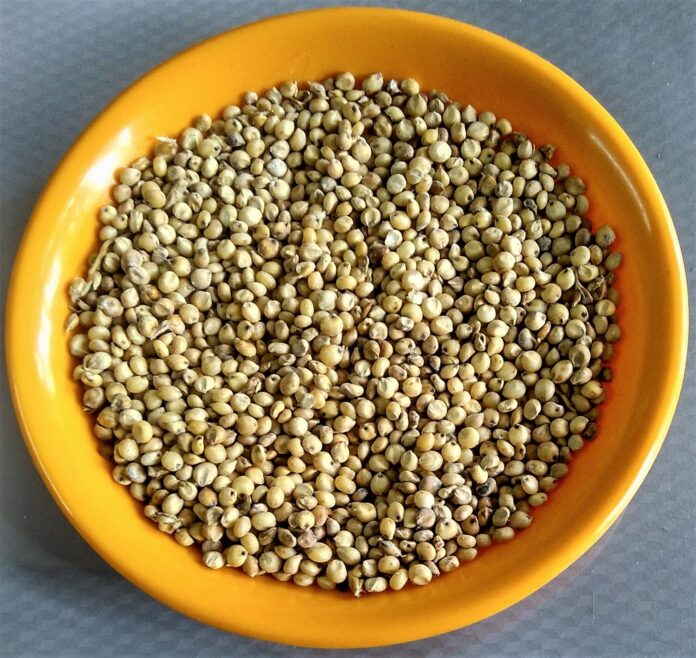
Sorghum has emerged as a standout grain in recent years, celebrated by nutrition experts, chefs, and sustainability advocates alike. Often dubbed a “supergrain,” sorghum is prized not only for its impressive nutritional profile but also for its versatility in the kitchen and its resilience in diverse growing conditions. Whether you’re looking for a gluten-free alternative or a nutrient-rich addition to your diet, sorghum offers a wealth of benefits that make it one of the favorite grains around the globe.
Nutritional Powerhouse
Sorghum is packed with essential nutrients that support overall health:
-
High in Fiber: With a robust fiber content, sorghum promotes digestive health by aiding in regular bowel movements and supporting a healthy gut microbiome.
-
Rich in Protein: As a complete protein source, sorghum provides all the essential amino acids required for muscle repair and overall cellular function.
-
Antioxidants: Sorghum contains antioxidants such as phenolic acids and flavonoids, which help neutralize free radicals and reduce oxidative stress.
-
Vitamins and Minerals: It’s a good source of B vitamins, iron, magnesium, and phosphorus—all of which play vital roles in energy production, bone health, and maintaining a strong immune system.
Research has shown that diets high in whole grains, like sorghum, are associated with a reduced risk of chronic diseases, including heart disease and type 2 diabetes. Its low glycemic index also means that sorghum can help maintain steady blood sugar levels, making it an excellent option for those with diabetes or anyone looking to sustain energy levels throughout the day.
Gluten-Free and Versatile
For those following gluten-free diets, sorghum is a welcome alternative to wheat and other gluten-containing grains. Its naturally gluten-free nature means it can be used safely by people with celiac disease or gluten sensitivities.
Culinary Versatility
Sorghum is incredibly versatile in the kitchen:
-
Whole Grain: Use cooked sorghum as a side dish or in salads to add a chewy texture and nutty flavor.
-
Flour: Sorghum flour is popular in gluten-free baking, helping to create breads, muffins, and pancakes with a unique, hearty taste.
-
Popped Sorghum: Similar to popcorn, popped sorghum is a fun, healthy snack.
-
Sorghum Syrup: A natural sweetener, sorghum syrup is rich in antioxidants and can be used in baking or as a topping.
Its adaptability makes it a favorite not only for health-conscious eaters but also for culinary enthusiasts who enjoy experimenting with new flavors and textures.
Sustainability and Environmental Impact
Sorghum isn’t just good for your body—it’s good for the planet, too. This grain is known for its exceptional resilience in challenging growing conditions, making it an eco-friendly choice.
Drought Resistance
-
Efficient Water Use: Sorghum is highly drought-resistant, meaning it requires less water compared to many other grains. This makes it especially valuable in regions where water is scarce.
-
Adaptability: It thrives in a variety of climates and soil types, contributing to food security and reducing the need for extensive irrigation.
Lower Carbon Footprint
-
Sustainable Farming Practices: Sorghum’s ability to grow in arid and semi-arid regions reduces the environmental impact of agriculture. Its low water and energy requirements help lower its overall carbon footprint.
-
Crop Rotation Benefits: When used in crop rotation systems, sorghum can improve soil health and reduce the reliance on chemical fertilizers, further supporting sustainable agriculture.
For environmentally conscious consumers, choosing sorghum aligns with a commitment to sustainability and responsible eating.
Health Benefits and Research
Numerous studies have highlighted the potential health benefits of incorporating sorghum into your diet:
-
Cardiovascular Health: Research published in the Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry indicates that sorghum’s antioxidant properties can help lower cholesterol levels and reduce the risk of heart disease.
-
Diabetes Management: Due to its low glycemic index, sorghum is less likely to cause spikes in blood sugar, making it a smart choice for managing diabetes.
-
Digestive Health: The high fiber content of sorghum supports a healthy digestive system and helps prevent constipation.
-
Anti-Inflammatory Effects: The bioactive compounds in sorghum have been shown to reduce inflammation, which is linked to a lower risk of chronic diseases.
These scientific findings affirm that sorghum is not only a nutritionally dense grain but also one that can play a significant role in promoting long-term health.
Tips for Incorporating Sorghum Into Your Diet
If you’re looking to boost your nutrition and contribute to a sustainable lifestyle, here are some practical ways to add sorghum to your daily meals:
Cooking with Whole Sorghum
-
As a Side Dish: Cook whole sorghum similarly to rice or quinoa. Simmer it in water or broth until tender, then fluff with a fork and season with herbs.
-
In Salads: Toss cooked sorghum with mixed greens, diced vegetables, and a light vinaigrette for a hearty salad.
-
Soups and Stews: Add cooked sorghum to soups and stews for extra texture and nutritional value.
Using Sorghum Flour
-
Baking: Substitute sorghum flour for a portion of wheat flour in recipes to make gluten-free bread, muffins, or pancakes. Combining it with other gluten-free flours can improve texture and flavor.
-
Thickening Agent: Use sorghum flour to thicken sauces and gravies, adding a subtle, nutty taste.
Snacking on Popped Sorghum
-
Healthy Snack: Pop sorghum kernels in a dry pan or air popper for a crunchy, low-calorie snack.
-
Mix with Nuts: Combine popped sorghum with nuts and dried fruit for a homemade trail mix that provides sustained energy.
Sweetening with Sorghum Syrup
-
Natural Sweetener: Replace refined sugars with sorghum syrup in baked goods, marinades, or as a drizzle over oatmeal. Its rich flavor and nutritional benefits make it a great alternative to traditional sweeteners.
Real-Life Success: Integrating Sorghum for Health and Sustainability
Consider the journey of Sarah, a nutrition-conscious professional who was looking for ways to improve her diet while being mindful of the environment. Sarah discovered sorghum as a versatile, nutrient-rich grain and began incorporating it into her meals. She started with a simple quinoa-sorghum salad, mixing the two grains for a unique texture and flavor. Over time, she experimented with sorghum flour in her baking and even enjoyed popped sorghum as a snack. Not only did she notice improvements in her energy levels and digestion, but she also felt good knowing she was choosing a sustainable food option that required less water and produced a lower carbon footprint.
Stories like Sarah’s highlight that adopting sorghum into your diet can lead to both personal health benefits and a positive impact on the environment. It’s a win-win scenario—enhancing your nutrient intake while contributing to a more sustainable food system.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q: Is sorghum gluten-free?
A: Yes, sorghum is naturally gluten-free, making it an excellent choice for those with celiac disease or gluten sensitivities.
Q: How does the nutritional profile of sorghum compare to other grains?
A: Sorghum is rich in protein, fiber, antioxidants, and essential minerals like iron and magnesium. It is comparable to quinoa and far superior to many refined grains in terms of nutrient density.
Q: Can I use sorghum in everyday cooking?
A: Absolutely! Sorghum is incredibly versatile. You can use it whole, as a flour in baking, or even pop it as a snack. Its mild, slightly nutty flavor pairs well with a variety of dishes.
Q: How can I enhance the absorption of nutrients from sorghum?
A: Pair sorghum with vitamin C-rich foods, such as citrus fruits or bell peppers, to enhance iron absorption. Also, cooking methods like steaming or light sautéing can help preserve the vitamins and minerals in sorghum.
Q: Where is sorghum primarily grown?
A: Sorghum is a staple crop in many parts of Africa, Asia, and the Americas. Its drought-resistant properties make it an important grain in arid regions around the world.
The Broader Impact of Choosing Sorghum
Beyond its nutritional benefits, sorghum represents a shift towards sustainable eating. In a world facing climate change and environmental challenges, choosing crops that require fewer resources and produce lower carbon emissions is more important than ever. By incorporating sorghum into your diet, you are not only supporting your own health but also contributing to a more sustainable, eco-friendly food system.
In addition, sorghum’s versatility means that it can be adapted to various cuisines and dietary preferences, from vegan and gluten-free diets to traditional comfort foods. This adaptability makes it a valuable addition to any pantry, offering both health benefits and culinary creativity.
Conclusion
Sorghum stands out as one of the favorite grains due to its impressive nutritional profile, versatility in the kitchen, and sustainable agricultural practices. Whether you’re using it as a whole grain in salads and side dishes, as a flour in gluten-free baking, or even as a crunchy, popped snack, sorghum offers numerous benefits for both health and the environment.
As we strive to maintain a balanced, nutrient-dense diet—especially in the face of aging, changing lifestyles, and environmental concerns—sorghum emerges as a powerful ally. Its ability to provide protein, fiber, antioxidants, and essential minerals makes it a key component for boosting energy, supporting digestion, and promoting overall well-being.
Embrace the benefits of sorghum in your daily meals and enjoy a versatile, sustainable superfood that supports both your health and the planet’s. Whether you’re a busy professional, an athlete, or someone simply seeking to improve your nutrition, incorporating sorghum into your diet can help you achieve your health goals—one delicious meal at a time.
Disclaimer
This article is for informational purposes only and does not constitute medical or nutritional advice. Always consult with a healthcare provider or registered dietitian before making significant changes to your diet, especially if you have underlying health conditions.