Diuretic foods promote urinary secretions, elimination of toxins, and are notably known to improve water retention and high blood pressure problems. vegetables, rich in water, fibre and minerals, stimulate the functioning of the kidneys and are therefore numerous to have these virtues. Beautyonfleeck list you 10 particularly diuretic vegetables to put on the menu.
Asparagus, diuretic and low in caloric
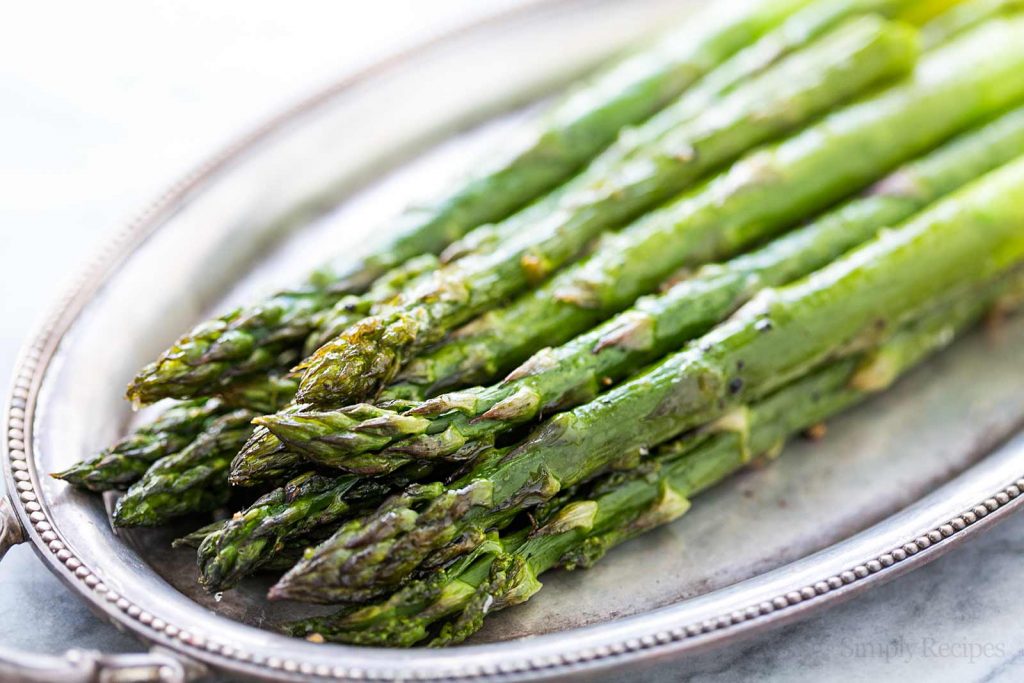

Asparagus is a very low calorie diuretic vegetable (21 calories for 6 full stems of canned and drained asparagus). They contain asparagine, a chemical that stimulates the functioning of the kidneys and helps them to get rid of the waste.
In addition, they have a very high antioxidant power (especially raw), which helps prevent the organism from many diseases. It is an excellent source of vitamin B9 (or folate) especially recommended for pregnant women as it prevents abnormalities of the neural tube, a congenital malformation that occurs between the 3rd and 4th week of pregnancy. It is also an excellent source of vitamin K, a vitamin that actively participates in blood clotting and helps prevent osteoporosis.
Asparagus is consumed in many ways: floods soaked in an aperitif sauce, steamed, boiled, baked or roasted.
Artichoke, an important source of antioxidants
The artichoke, appreciated as much for its leaves as for its heart, is diuretic thanks to its content of fibres, minerals and vitamins that help the kidneys to function well and encourage the evacuation of excess water and salt.
In addition, the edible parts of the artichoke contain a wide variety of antioxidants, beneficial to health. It is an excellent source of copper, necessary for the formation of hemoglobin and collagen (protein used for tissue structure and repair). It would also have benefits on hypercholesterolemia by reducing total cholesterol and bad cholesterol (LDL) while increasing good cholesterol (HDL).
The artichoke can be eat cooked, stuffed, or incorporated into recipes of pies, clafoutis, doughnuts…
The carrot, for the prevention of eyes diseases
The carrot, diuretic due to its potassium richness (320 mg potassium).
The many pigments in the carrot would help prevent several diseases, including cardiovascular disease (a study done with carrot juice) and some cancers, including lung cancer. It would also reduce the prevalence of cataracts in men and women, due to its content in alpha, beta-carotenes, lutein and zeaxanthin. The darker the color, the more it is rich in beta-carotene (the brown carrots contain twice as much as the orange carrots).
Carrots are consumed raw or cooked, grated, puréed, soup, cake, roasted… and for people who wish to lose weight, crunching 1 or 2 raw carrots is a good appetite suppressant.
Broccoli to reduce cardiovascular risk
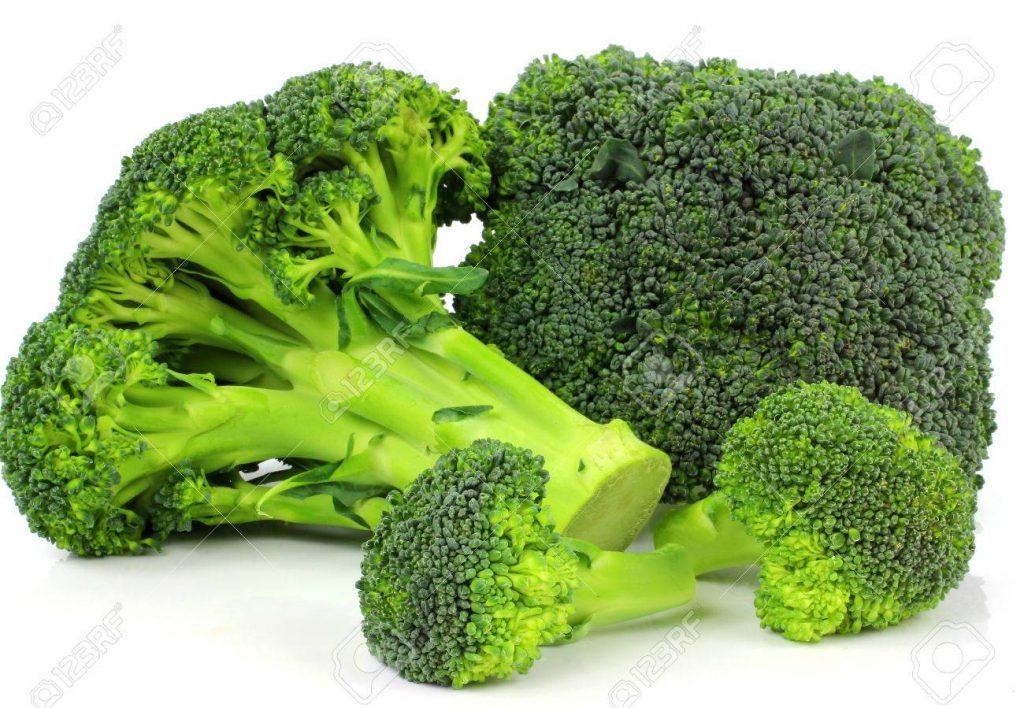

Due to its high mineral content such as magnesium (21 mg for 100 g) and potassium (316 mg for 100 g), broccoli is a diuretic vegetable.
It contains a lot of vitamin C – which has strong antioxidant properties – and vitamin K. Consumed at least a few times a week, this vegetable would be associated with a lower risk of colorectal cancer, stomach, lung, prostate and even Breast in the woman premenopausal. It would also contribute to the maintenance of good cardiovascular health and is even recommended in type 2 diabetics to increase their concentration of good cholesterol and reduce triglyceride levels and bad cholestérol.
Broccoli can be eaten raw or cooked, in salads, in soup or even in an omelette, quiche or other salty preparation. To make the most of its benefits, it is best to consume it raw or lightly cooked.
Eggplant to reduce blood lipid levels
Eggplant is a vegetable that belong to the Solanaceae family and is characterized by its purple peel, although there are yellow, green and even white varieties. Its richness in water, fibre, potassium (229 mg for 100 g) and magnesium (14 mg for 100 g) make it a diuretic vegetable.
It is a very low calorie vegetable (29 calories for 84 g of boiled eggplant drained) and rich in antioxidants, which reduce the damage caused by free radicals in the body. According to a study, it would contribute to the reduction of blood lipid levels. It is also a source of manganese when it is consumed raw, a source of copper, vitamins B1 and B6.
Eggplant can be eaten fried , stuffed, in ratatouille or in vegetable curries.
The antioxidant virtues of zucchini
The zucchini, composed of 95% water, rich in magnesium (18 mg for 100 g) and potassium (261 mg for 100 g), is part of the diuretic vegetables.
It contains rutin, a phenolic compound of the flavonoid family, which has some antioxidant activity that can protect against LDL cholesterol and oxidation. The carotenoids (and in particular lutein and zeaxanthin) which it contains would also have an antioxidant action, in addition to preventing certain eyes diseases. Zucchini is a moderate source of many nutrients such as phosphorus, magnesium, potassium, iron or vitamins B1, B2, B6, B9, i.e. a portion provides between 5 and 15% of the recommended intake of these nutrients.
Zucchini can be eaten raw soaked in a sauce, in salad, or cooked, sautéed, fried, in soup… It is recommended to consume zucchini with the skin to keep all the nutrients.
Celery, against high blood pressure
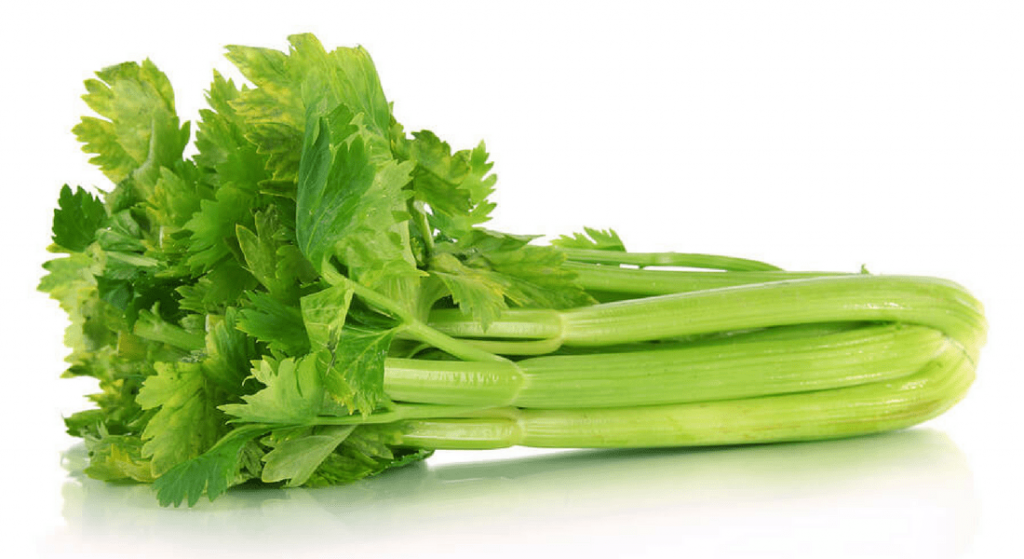

Tender and crisp at the same time, celery is a diuretic vegetable known for its low calorie content (6 calories for a medium branch of raw celery of 40 g and 14 calories for 80 g of celery boiled and drained). It owes its diuretic action to its high potassium content (260 mg per 100 g), counterbalancing its high sodium content (80 mg per 100 g).
The polyacetylenes found in celery could prevent the proliferation of several types of cancer cells, as suggested by a study conducted in 2006. Boiled and drained, it is also an excellent source of vitamin K and a good source of vitamin B6.
Celery can be eaten raw as a snack, salad, juice with tomatoes and carrots, cooked in soups, sauces, stews, quiches or vegetable planters. The high sodium content of celery, balanced by its high potassium content, makes it an interesting salty food for people suffering from hypertension whose salt intake must be limited.
Cabbage, prevention of oxidative stress
Cabbage and its many varieties, but especially Brussels sprouts, because of its high fiber and potassium (389 mg per 100 g), have diuretic properties.
The phytochemicals of cabbage (especially glucosinolates) would stimulate the immune system, prevent oxidative stress, the onset of cancer and reduce the proliferation of cancer cells. Cabbage and boiled red cabbage are an excellent source of vitamin K.
Cabbage can be eaten cooked or raw, stuffed, braised, soup … To preserve its benefits against cancer, it is better to consume raw or slightly cooked.
Red beet would decrease the appearance of certain cancers
Diuretic due to its potassium content (about 300 mg for 100 g), red beet is considered a superfood, and because of this, it is rich in antioxidants. It is also one of the only vegetables with such a high antioxidant power.
It contains phenolic compounds, including flavonoids, which maintain its antioxidant power even after baking. Betanin, one of its components, would reduce the appearance of certain cancers and have cytotoxic effects – cytotoxic agents either destroy cells or prevent their multiplication – on breast and prostate cancer. It is an excellent source of vitamin A – which contributes to the growth of bones and teeth and promotes good vision in the dark – and vitamin K.
Red beet can be consumed raw, in appetizer, in salad, grated, baked or steamed. Its leaves are eaten raw or cooked like those of spinach.
Cucumber, ideal for calorie diets
Cucumber is a diuretic and refreshing vegetable, especially appreciated in the warmer seasons. It owes its diuretic properties to its water richness and its large amount of silicon and sulfur, which stimulate and help the kidneys to get rid of uric acid.
Raw, it is composed of 95% water, which makes it ideal for people who monitor their weight: 63 g of raw cucumber with or without peel represent 9 and 8 calories, respectively. The raw cucumber without its peel is a source of copper, and, with its peel, vitamin K. It also has slightly antioxidant properties, due to the presence of phenolic compounds.
The cucumber is basically consumed raw, in salad or in appetizer, with a yogurt and herbal sauce, but it can also be cooked and consumed like zucchini.