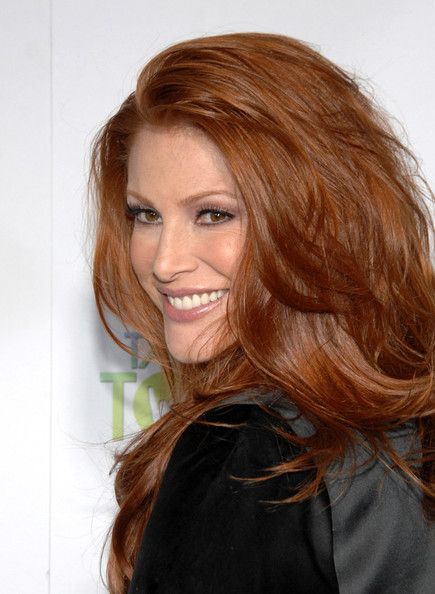
Angie Everhart has been a supermodel, an actress and a reality TV star , she was diagnosed with thyroid cancer in 2013 after going in for what she thought was a routine MRI to assess some pain she had been feeling in her shoulder.
It is 2.9-times more common in women than men . There are different types of thyroid cancer, but most of these cancers can be treated successfully.
Symptoms of thyroid cancer
Neck lump
- Often it causes a painless lump or swelling low down in the front of the neck.
Other symptoms
- swollen glands in the neck.
- unexplained hoarseness that doesn’t get better after a few weeks.
- a sore throat that doesn’t get better.
- pain in your neck.
- difficulty swallowing.
- breathing difficulties.
You Can Also Read : Sleep Paralysis….The Awake Nighmare
Potential Risk Factors
Gender and Race-related risks
- Females are affected 2 to 3 times more often than males.
- People who are white or Asian are more likely to develop thyroid cancer.
Age and Family-related risks
- Most cases of thyroid cancer affect people between the ages of 20 and 55.
- Multiple Endocrine Neoplasia, or multiple endocrine tumors (MEN2A and MEN2B) are tumors that affect glands of the endocrine system (eg, thyroid, parathyroid, adrenal). In rare cases, people have a family history of medullary thyroid cancer.
- According to the American Society of Clinical Oncology, anaplastic thyroid cancer is usually diagnosed adults older than 60.2
- Although rare, medullary thyroid cancer may develop in infants 10 months and older and during adolescence if the child carries the RET proto-oncogene* mutation.2
*DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) makes up each person’s biological blueprint. Genes are parts of the DNA that are inherited. An oncogene is a gene that has mutated and has the potential to cause cancer. Proto-oncogenes are genes that have mutated and can cause a cancer at the cellular level. There are different types of proto-oncogenes, such as RET.
Radiation Exposure
- Routine x-rays such as those performed during a dental examination or mammography do not cause thyroid cancer.
How is it treated?
- a thyroidectomy – surgery to remove part or all of the thyroid.
- radioactive iodine treatment – you swallow a radioactive substance that travels through your blood and kills the cancer cells.
- external radiotherapy – a machine is used to direct beams of radiation at the cancer cells to kill them.
- chemotherapy and targeted therapies – medications used to kill cancer cells.
You Can Also Read : 8 Causes of Night Sweats